Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Integer vel eros volutpat, consequat diam ac, eleifend dolor. Mauris risus ante, tempus in interdum elementum, consectetur id odio. Praesent lorem dolor, sollicitudin sed metus at, laoreet vestibulum dolor.
ALPINI, Prospero (ALPINO, 1553–1617) & BONDT [BONTIUS], Jacob de (1591–1631)
De medicina Ægyptiorum, libri quatuor & Jacobi Bontii, De medicina Indorum. Editio Ultima.
Paris, Nicolas Redelichuysen, 1645.
Bound together with Aselli’s De lactibus (1628).
-
More info
-
More info

-
More info

-
More info

-
More info
-
More info

Related items
-

ALPINI, Prospero (ALPINO, 1553–1617) & BONDT [BONTIUS], Jacob de (1591–1631)
De medicina Ægyptiorum, libri quatuor & Jacobi Bontii, De medicina Indorum. Editio Ultima.
Paris, Nicolas Redelichuysen, 1645.
Bound together with Aselli’s De lactibus (1628). -

CASSERIO, Giulio (c. 1552–1616)
Tabulæ anatomicæ LXXIIXX. Omnes novæ nec ante hac visæ. Daniel Bucretius XX. quæ deerant supplevit & omnium explicationes addidit. [Tabulae anatomicae]
Francofurti, Matthæi Mer... -

BONDT [BONTIUS], Jacob de (1592–1631)
De medicina Indorum Lib. IV.
1. Notæ in garçiam ab orta.
2. De diæta sanorum.
3. Meth. medendi Indica.
4. Observationes e cadaveribus.
Lugdunum Batav., Franciscum Hacki... -

STENO, Nicolaus [NIELS STENSEN (1636–1686)]
Elementorum myologiæ specimen, seu musculi descriptio geometrica. Cui accedunt canis carchariæ dissectum caput, et dissectus piscus ex canum genere.
Florentiæ, (Fr. Iacobus Tos...
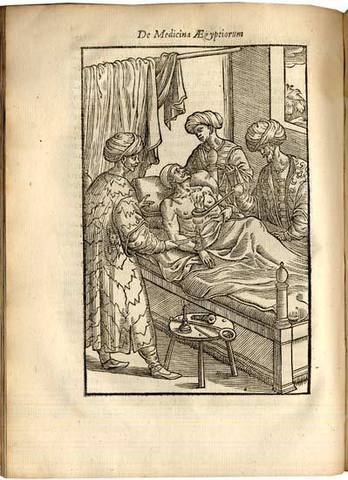
First published in Venice 1591, this was “the first important work on the history of Egyptian medicine, and one of the earliest European studies of non-Western medicine. Alpini’s work dealt primarily with contemporary (i.e. Turkish) practices observed during a three-year sojourn in Egypt. These included moxibustion – the production of counter-irritation by placing a burning or heated material on the skin – which Alpini introduced into European medicine; the technique is illustrated in a full-page woodcut of f. 101 verso. Alpini also mentioned coffea for the first time in this work, under the names of “bon” and “chaoua”.” (Norman). Alpini became professor of botany at Padua after having spent three years in Egypt. The present edition also contains Jacob de Bondt’s De medicina Indorum, which was first published in Leiden, 1642. Bondt was probably the first to regard tropical medicine as an independent branch of medical science. He spent the last four years of his life in the Dutch East Indies and the book includes the first modern description of beri-beri and cholera. Bondt’s work is also found in Piso’s De Indiae utriusque re naturali et medica (1658), the revised edition of Piso’s Historia naturalis Brasiliæ.
Collation: Pp. (11), 150, (25); de Bondt: pp. 39, (1). Alpini has 7 woodcuts in the text of which 2 are fullpage (moxibution). Title printed in red and black.
Binding: Contemporary vellum.
Provenance: Signature on title of the first work in the volume, Aselli’s De lactibus, 1628: Johan Linder (1676–1723, ennobled Lindestolpe, see note for Aselli). Inscription inside back cover: Stockh. d 30 Octobr 1712.
References: Garrison-Morton 6468 (Alpini) & 2263 (Bondt) for the first editions; DSB I, pp 124-5 (Alpini). Waller 12509 (1st ed.) & 12510 (Ed. nova, 1719).